Book Appointment Now
Innovative Treatments for Pleural Effusions: From Diagnosis to Recovery
Pleural effusions, the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, can significantly impact a person’s breathing and overall health. This condition can arise from various underlying causes, including infections, heart failure, and malignancies. Managing pleural effusions effectively requires accurate diagnosis and innovative treatment approaches to alleviate symptoms and improve patient outcomes. In this blog, we will explore the latest advancements in diagnosing and treating pleural effusions, highlighting how these innovations are transforming patient care from diagnosis to recovery.
Understanding Pleural Effusions
Pleural effusions occur when excess fluid builds up in the pleural space, the thin gap between the lungs and the chest wall. This buildup can compress the lungs, making it difficult to breathe and causing discomfort. The causes of pleural effusions are diverse and include:
- Infections: Bacterial pneumonia and tuberculosis can lead to pleural effusions as the body reacts to infection by accumulating fluid in the pleural space.
- Heart Failure: When the heart fails to pump blood effectively, fluid can back up into the lungs and pleural space, causing effusions.
- Malignancies: Cancers, particularly lung and breast cancer, can cause pleural effusions either by spreading to the pleura or by blocking lymphatic drainage.
- Liver or Kidney Disease: These conditions can lead to fluid imbalances in the body, resulting in pleural effusions.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot in the lungs can cause inflammation and fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
Common symptoms of pleural effusions include shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, and fever. If left untreated, pleural effusions can lead to complications such as lung collapse, infection, and respiratory failure. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of pleural effusions.
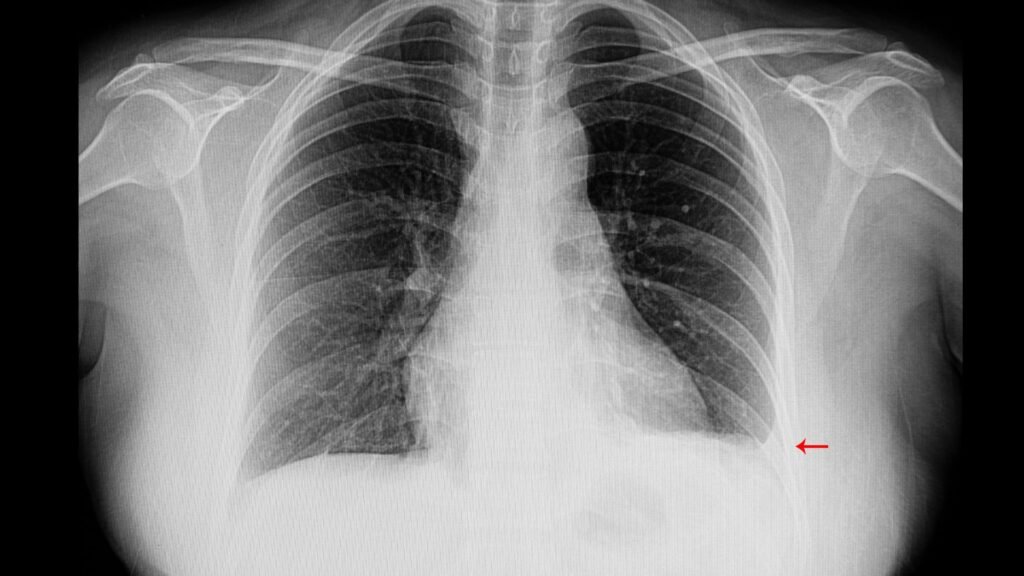
Diagnosing Pleural Effusions
Accurate and timely diagnosis of pleural effusions is essential for effective treatment. Several diagnostic tools and techniques are used to identify the presence and underlying cause of pleural effusions:
- Chest X-ray: A standard imaging test that can reveal fluid accumulation in the pleural space. It is often the first step in diagnosing pleural effusions.
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique uses sound waves to create detailed images of the pleural space, helping to detect and evaluate the extent of fluid buildup.
- CT Scan: A more detailed imaging test that provides cross-sectional views of the chest, allowing for precise assessment of the pleural effusion and identification of any underlying abnormalities.
- Thoracentesis: A procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space to remove a sample of the fluid for analysis. This test helps determine the cause of the effusion by examining the fluid’s characteristics and identifying infections, malignancies, or other conditions.
- Pleural Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy of the pleura may be necessary to diagnose the cause of the effusion, especially if malignancy is suspected. This involves taking a small tissue sample from the pleura for examination under a microscope.
Early and accurate diagnosis using these techniques is crucial for guiding appropriate treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Conventional Treatment Approaches
Traditional treatments for pleural effusions focus on relieving symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. Some of the common conventional treatment approaches include:
- Thoracentesis: This procedure involves inserting a needle into the pleural space to drain excess fluid. It provides immediate relief from symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest pain. However, it may need to be repeated if the underlying cause of the effusion is not addressed.
- Chest Tube Placement: For larger or recurrent pleural effusions, a chest tube may be inserted to continuously drain fluid from the pleural space. This is often done in a hospital setting and can help manage more severe cases.
- Medical Management: Treating the underlying cause of the pleural effusion is essential. This may involve antibiotics for infections, diuretics for heart failure, or chemotherapy for cancer-related effusions.
- Pleurodesis: This procedure involves introducing a sclerosing agent into the pleural space to cause the pleural layers to stick together, preventing the reaccumulation of fluid. It is commonly used for recurrent pleural effusions, particularly those related to malignancies.
While these conventional methods can be effective, they may have limitations, such as the need for repeated procedures or the inability to completely prevent fluid reaccumulation. Recognizing these challenges has driven the development of more innovative treatments to improve patient outcomes.
Innovative Treatment Options
Recent advancements in medical technology have led to the development of innovative treatments for pleural effusions. These modern techniques offer minimally invasive options and improved outcomes for patients:
- Thoracoscopy: Also known as video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), this minimally invasive procedure allows doctors to examine the pleural space with a camera and perform necessary interventions, such as biopsies or pleurodesis. Thoracoscopy offers a more comprehensive approach compared to traditional methods and can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
- Indwelling Pleural Catheter (IPC): An IPC is a flexible tube that is inserted into the pleural space to allow for continuous drainage of fluid at home. This option is particularly beneficial for patients with recurrent pleural effusions, as it provides long-term relief and reduces the need for repeated hospital visits.
- Medical Thoracoscopy: A procedure performed under local anesthesia that combines diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. It allows for direct visualization of the pleural space, biopsy collection, and pleurodesis in a single session, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery.
- Pleurodesis: Advances in pleurodesis techniques, such as using talc powder or other agents, have improved the efficacy of this procedure. Pleurodesis can now be performed via thoracoscopy or through a chest tube, reducing the likelihood of fluid reaccumulation and providing lasting relief.
These innovative treatments represent significant strides in managing pleural effusions, offering patients more effective and less invasive options to improve their quality of life.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Care
Managing pleural effusions effectively requires a multidisciplinary approach that involves collaboration among various healthcare specialists. This team-based care ensures comprehensive evaluation and treatment, addressing all aspects of the patient’s condition:
- Pulmonologists: Specialize in diagnosing and treating respiratory conditions, including pleural effusions. They play a crucial role in determining the underlying cause of the effusion and recommending appropriate treatment options.
- Thoracic Surgeons: Perform surgical interventions such as thoracoscopy, chest tube placement, and pleurodesis. Their expertise is essential for cases requiring surgical management.
- Radiologists: Provide critical imaging support for diagnosing pleural effusions and guiding procedures like thoracentesis and catheter placement.
- Oncologists: In cases where pleural effusions are related to cancer, oncologists manage the overall cancer treatment plan and coordinate with other specialists to address the effusion.
- Nurses and Respiratory Therapists: Offer supportive care, educate patients about their condition and treatment options, and assist with procedures and post-treatment recovery.
This multidisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive holistic care, improving treatment outcomes and enhancing the overall management of pleural effusions.
Patient Experience and Recovery
Understanding what to expect during and after treatment for pleural effusions can help patients feel more comfortable and prepared. Here’s an overview of the patient experience and recovery process:
- During Treatment: Depending on the chosen treatment method, the procedure may be performed under local or general anesthesia. Patients might feel some pressure or discomfort, but pain is generally well-managed. Minimally invasive procedures like thoracoscopy or the placement of an indwelling pleural catheter typically result in less pain and faster recovery times compared to traditional surgery.
- After Treatment: Post-procedure, patients are monitored to ensure there are no complications such as infection or pneumothorax. Pain management, breathing exercises, and careful monitoring of fluid drainage are essential parts of the recovery process.
- At Home: Patients with an indwelling pleural catheter can manage fluid drainage at home, reducing hospital visits. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Tips for Recovery: Staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, avoiding strenuous activities, and practicing good respiratory hygiene can aid in a smoother recovery. Patients are encouraged to report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly.
Innovations and Future Directions
The field of pleural effusion treatment is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and technological advancements aimed at improving patient outcomes. Future directions in managing pleural effusions include:
- Biomarker Research: Identifying specific biomarkers in pleural fluid can help diagnose the underlying cause of effusions more accurately and tailor treatment strategies accordingly.
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: Advances in imaging technology, such as high-resolution CT scans and MRI, can provide more detailed views of the pleural space, aiding in precise diagnosis and intervention planning.
- Robotic-Assisted Thoracoscopy: The integration of robotics into thoracoscopic procedures can enhance precision, reduce invasiveness, and improve recovery times.
- Gene Therapy and Targeted Treatments: Emerging therapies aimed at addressing the underlying genetic and molecular causes of pleural effusions hold promise for more effective and personalized treatments.
Pleural effusions can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, but with accurate diagnosis and innovative treatment options, effective management is possible. By staying informed about the latest advancements and working closely with a multidisciplinary team, patients can achieve better outcomes and improved overall health. The continued evolution of medical technologies and techniques offers hope for even more effective treatments in the future.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of pleural effusion, don’t hesitate to seek expert care. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Ritesh to discuss your condition and explore the most advanced and appropriate treatment options for you. Visit our website or contact our clinic today to book an appointment and take the first step towards better respiratory health and improved quality of life.


